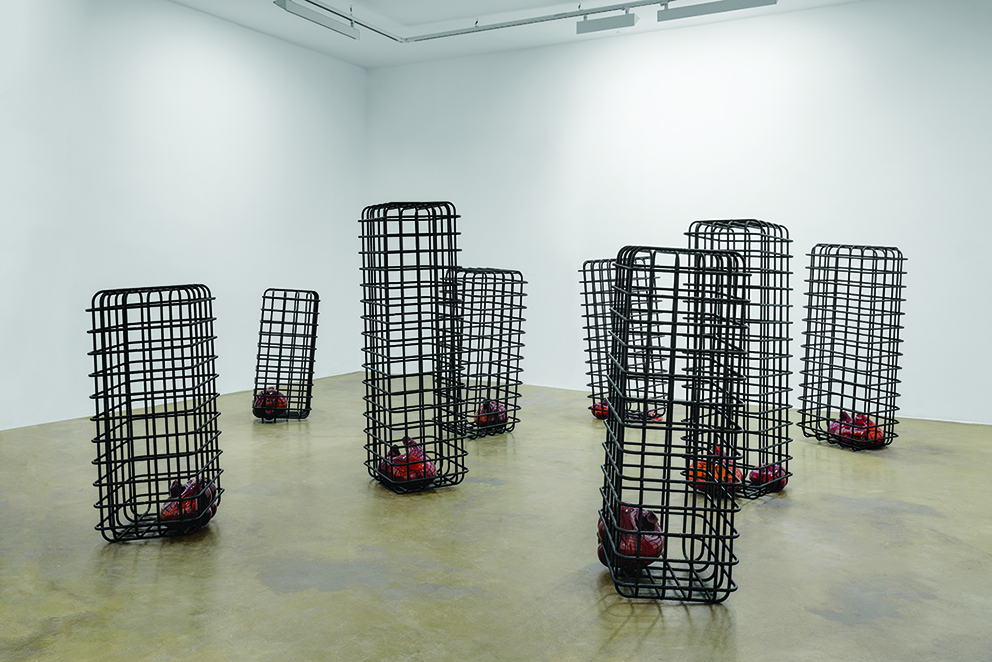
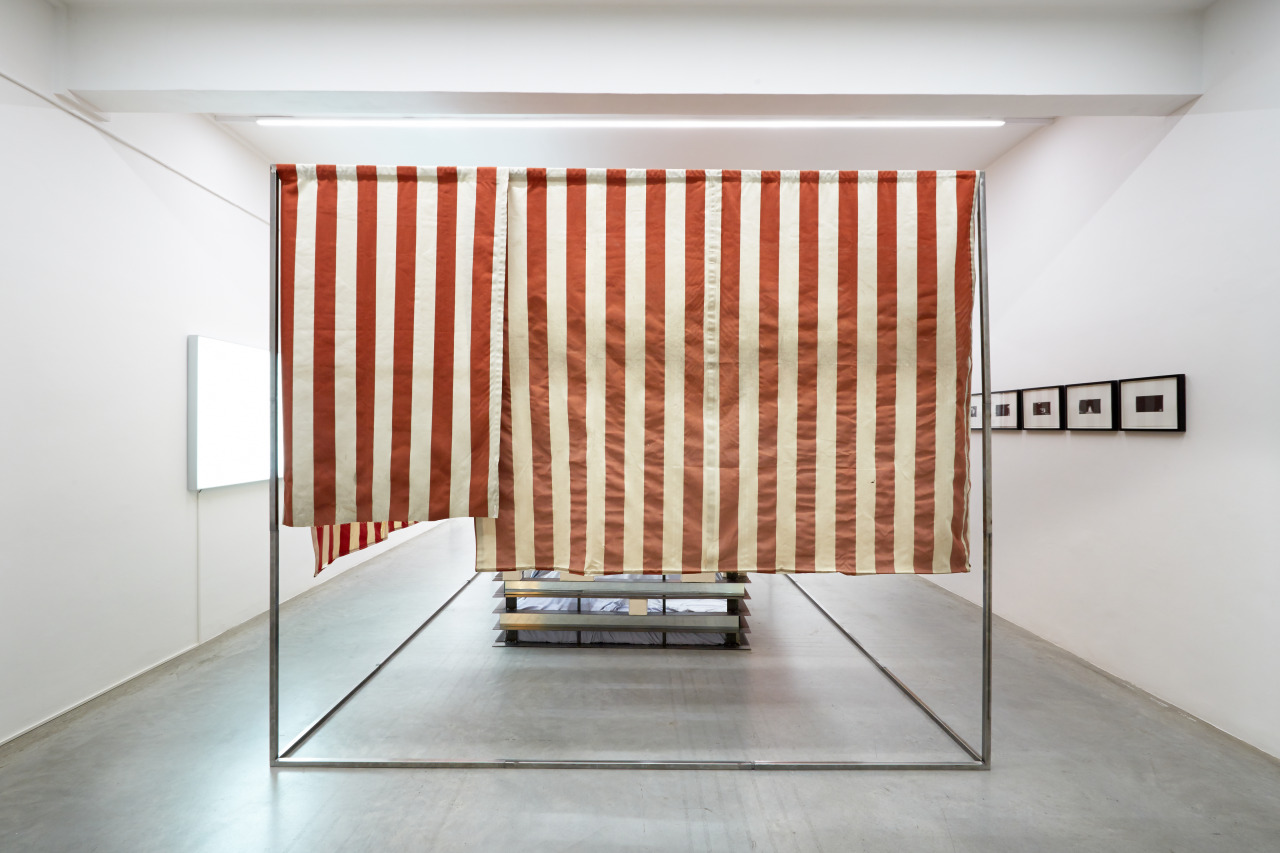
Mario Merz
London, Pace Gallery
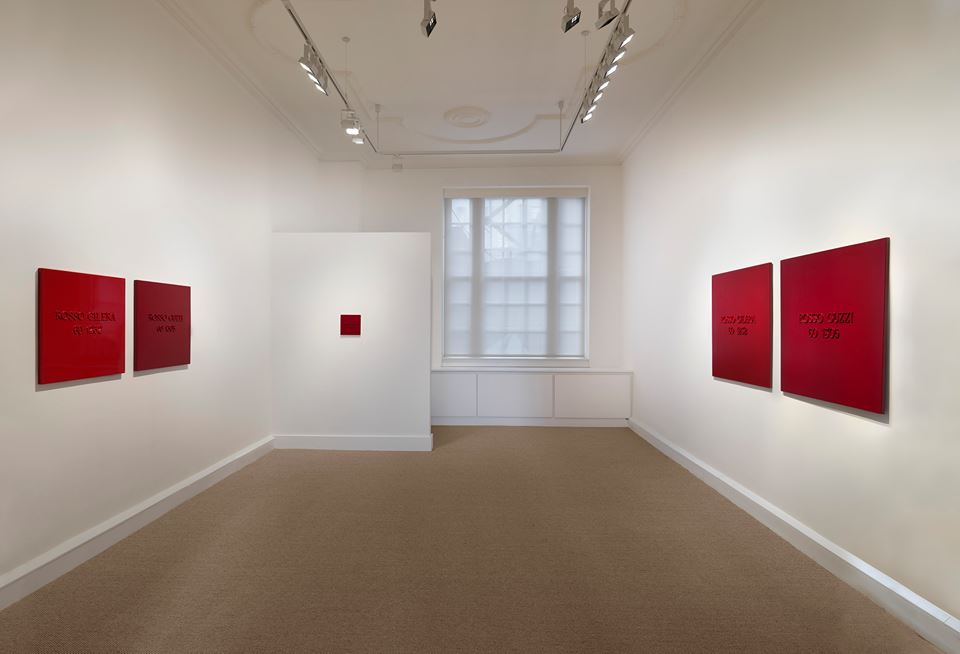
Pace London, in collaboration with Fondazione Merz, is honoured to present a momentous exhibition of the late Italian artist Mario Merz from 26 September to 8 November 2014 at 6 Burlington Gardens. Featuring works from the 1960s to 2003, this retrospective marks the first major UK gallery staging of the artist’s work in more than twenty years and Pace’s first exhibition of Merz’s work.
Merz reacted against the dominant trends in art from the 1950s and 1960s, rejecting the mythic aspirations of movements like Abstract Expressionism in favour of a more grounded art rooted in simple materials and nature, prompting his inclusion in Italy’s loosely organised Arte Povera movement. Merz’s presiding interest throughout his career was the transformation of materials by placing them in contact with alternate forces of energy, drawing his art into a more organic state. “I work from the emotions I get from the archetypal structure that cancels the material. Then, once I have procured the object I try to take possession of its structure with my hands, arranging it in various positions till I feel it is in unison with me physically…,” Merz said. “In fact the point of my work is to regain possession of ‘things’, by avoiding filling them out with projections, and to keep their limited but individual primary presence alive in myself.” This preoccupation—what curator Harald Szeeman called Merz’s “interior necessity”—inspired the range of Merz’s formal motif, including the igloo, nature, tables, neon lighting, and the Fibonacci sequence, all of which feature in the exhibition.
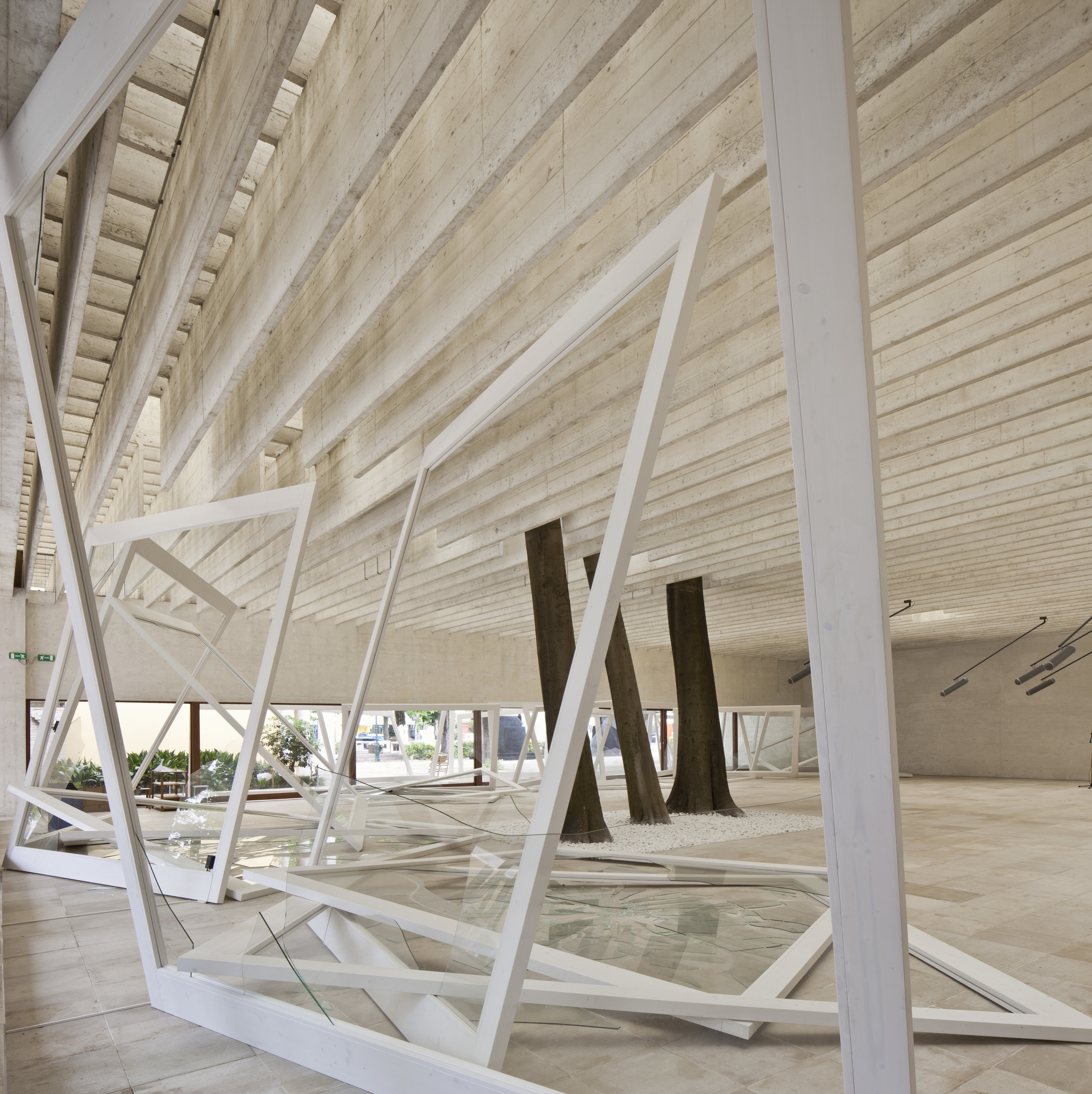
The exhibition’s centerpiece is Spostamenti della Terra e della Luna su un Asse (Movements of the Earth and the Moon on an Axis) (2003), a three-domed installation and the final igloo he made. Merz began constructing igloos in 1968 using a variety of materials, and this particular one combines many of these earthen and industrial objects—metal rods, neon, clamps, clay, glass and stone—in its tripartite structure. Merz’s igloos are among his most iconic works, providing a free-standing and independent form to affect material energies, however impermanent or precarious they may be. “For him it is the act of building, not the finished structure that is meaningful. Building is a journey through the territory he works in, so his process is determined by the conditions he finds, his materials—whether man-made or natural—depend upon what is locally available,” wrote curator Germano Celant.
The artist’s interest in light and energy found its most enduring expression in his use of neon tubes. Merz employed neon lights on materials such as bottles, synthesizing the industrial qualities of the tube with the chemical and its immaterial radiance. In Igloo con vortices (Igloo with Vortex) (1981), on public view for the first time since his 1989 retrospective at the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, New York, Merz placed a blue neon light amidst a swath of bundled brushwood leaning against a mixed media rendering of a cone and dome. “The neon is experienced as an energetic flux or spear of light that passes through the object, thus destroying the idea of the solidity of the object,” wrote Celant. “Punctured by the neon, the object becomes annulled as an icon but it is redefined as material; the neon abandons its own physicality and becomes light.”
Merz also used neon in Linea (Line) (1991), a work that straddles the line between painting and sculpture, depicting the first nineteen terms of the Fibonacci sequence in blue neon on a raw canvas suspended from a metal frame. The mathematical sequence, in which each term is determined by the sum of the two previous values, became a hallmark of the artist’s practice for its resonance with both the spiral and nature, as many interlocutors have cited Fibonacci’s sequence as mirroring organic patterns. Spirals recur in several works in the exhibition, including the sprawling, installation Une Ouvrée, une mesure de terre qui donne un portrait bien terrestre (1986), a rectilinear spiral of mesa-like concrete blocks and firewood on view on the gallery’s second floor. The spiral functioned as an allegory for growth and development, spawning outward to grow and incorporate more space, but also change its form and energy. “If you make an assemblage, you create a sort of concentrated power that transmits a naturally more optic emotion, but also a feeling of presence.” The spiral echoes the tables Merz made and painted throughout his career, which served as a stage for his assemblages but also connected to broader formal and conceptual ideas of line and space. “I reject linear, one by one, or assembly-line fabrication of spaces. I reject the idea that there can be a fixed number of people in a space,” Merz wrote in 1973.
The exhibition includes sculptures and works on paper that express some of his most enduring motifs. Merz’s interest in art emerged during his imprisonment in 1945, while detained for anti-Fascist activities he began regularly drawing spiraling forms without lifting his pen from the page. These activities combined with his reaction against the Italian state informed his desire to defy the status quo of art through a turn toward simpler materials and imagery. The works on paper, although drawn from various points in his life, speak to Merz’s sustained investment in the ideas that inspired his art, depicting spirals as well as organic form with a range of materials and objects such as raincoats, which became a hallmark of many of his mixed media and two-dimensional works. These works, and the exhibition as a whole, attest to his pursuit of a distinctive and avant garde project steeped in new ways of making art. Merz said, “I think that everything has already been destroyed and, as far as I’m concerned, I want to put things right again, really clean things out.”
For more information please visit: www.pacegallery.com